Culture Of Lithuania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Culture of Lithuania combines an indigenous heritage, represented by the unique
 Lithuania has the most homogeneous population in the
Lithuania has the most homogeneous population in the
 Since the
Since the
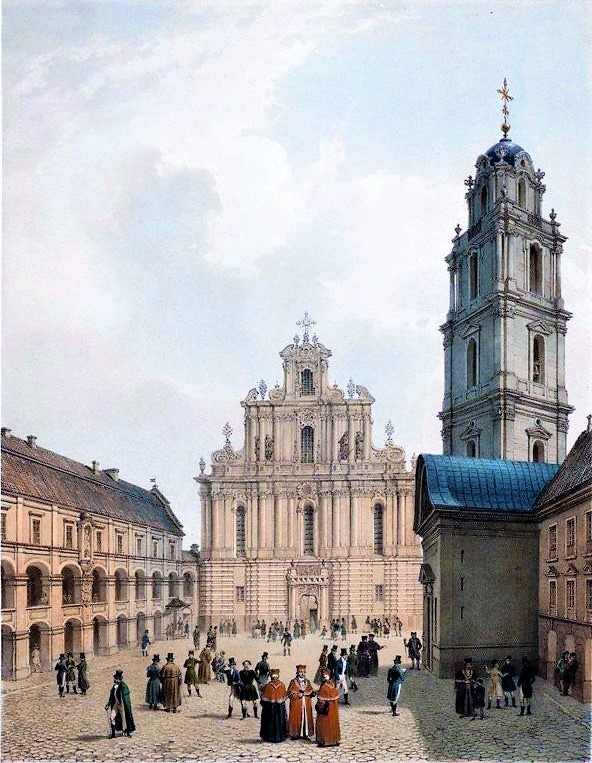 Education in Lithuania exists from pre-school to adult education. Colleges and universities in Lithuania have undergraduate and higher education. Pre-school is for children aged three to six years. After pre-school, children enroll in primary school from seven to ten years of age. At eleven, students begin secondary school until the age of 18. Once the general education is completed, students go to college or university. Students can take the UK exam to study overseas. A bachelor's degree takes four years, traditionally, to complete. A master's takes one to two years to complete; and a doctoral degree takes four years. Lithuania's oldest university is
Education in Lithuania exists from pre-school to adult education. Colleges and universities in Lithuania have undergraduate and higher education. Pre-school is for children aged three to six years. After pre-school, children enroll in primary school from seven to ten years of age. At eleven, students begin secondary school until the age of 18. Once the general education is completed, students go to college or university. Students can take the UK exam to study overseas. A bachelor's degree takes four years, traditionally, to complete. A master's takes one to two years to complete; and a doctoral degree takes four years. Lithuania's oldest university is
 Lithuanian cuisine features the products suited to its cool and moist northern climate:
Lithuanian cuisine features the products suited to its cool and moist northern climate:

 Lithuania's art community is famous for
Lithuania's art community is famous for
Antanas Tranyzas: The Amber Museum of Palanga
Retrieved on March 29, 2007. The
 Lithuanian folk music is based around songs (), which include romantic, wedding songs, as well as work songs and more archaic war songs. Traditional vocal music is held in high esteem on a world scale: Lithuanian song fests and multipart songs are on the
Lithuanian folk music is based around songs (), which include romantic, wedding songs, as well as work songs and more archaic war songs. Traditional vocal music is held in high esteem on a world scale: Lithuanian song fests and multipart songs are on the
 Lithuania has a lively drama scene. Many
Lithuania has a lively drama scene. Many
Lithuanian Academy of Music and Theatre. Retrieved on October 17, 2008. Several directors are important to Lithuania's theatre scene.
 There are eighty Olympic and non-Olympic sports federations in Lithuania. Among the most popular sports in Lithuania are
There are eighty Olympic and non-Olympic sports federations in Lithuania. Among the most popular sports in Lithuania are  Lithuania's national basketball team,
Lithuania's national basketball team,
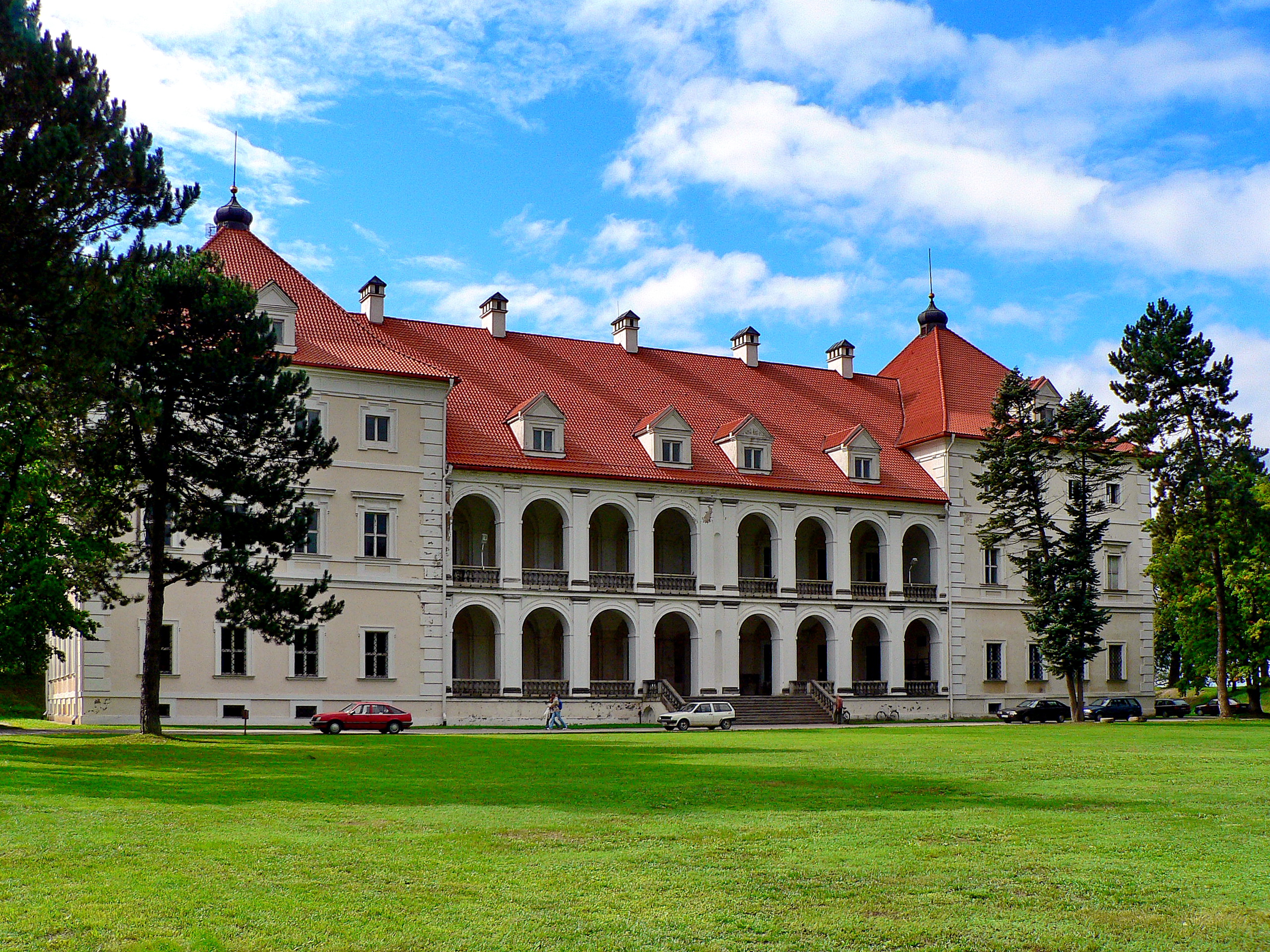 Several famous Lithuania-related architects are notable for their achievements in the field of architecture.
Several famous Lithuania-related architects are notable for their achievements in the field of architecture.
 The official holidays are found in Article 162 of the ''Labour Code of the Republic of Lithuania.'' The holidays are as follows:
* January 1:
The official holidays are found in Article 162 of the ''Labour Code of the Republic of Lithuania.'' The holidays are as follows:
* January 1:
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian ( ) is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.8 millio ...
, with Nordic cultural aspects and Christian traditions resulting from historical ties with Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
. Although linguistic resemblances represent strong cultural ties with Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
in various historical moments Lithuania was influenced by Nordic, Germanic and Slavic cultures. Various cultural changes occurred throughout Lithuania's transformation from a country occupied by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
to an independent Baltic state
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
.
Ethnicity and nationality
Baltic states
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
. In the 2001 census, 83.45% of the population identified themselves as ethnic Lithuanians, 6.74% as Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
, 6.31% as Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, 1.23% as Belarusians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5–10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000–768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
, and 2.27% as members of other ethnic groups. Poles in Lithuania
The Poles in Lithuania ( pl, Polacy na Litwie, lt, Lietuvos lenkai), estimated at 183,000 people in the Lithuanian census of 2021 or 6.5% of Lithuania's total population, are the country's largest ethnic minority.
During the Polish–Lithuanian ...
are concentrated in the Vilnius Region
Vilnius Region is the territory in present-day Lithuania and Belarus that was originally inhabited by ethnic Baltic tribes and was a part of Lithuania proper, but came under East Slavic and Polish cultural influences over time.
The territor ...
, allowing Electoral Action of Poles in Lithuania
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated ...
, their ethnically-based party, to exert some influence. Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, however, are relatively evenly spread throughout Lithuania. Lithuanians are usually divided into 5 groups: Samogitians
Samogitians ( Samogitian: ''žemaitē'', lt, žemaičiai, lv, žemaiši) are an ethnographic group of Lithuanians of the Samogitia region, an ethnographic region of Lithuania. Many speak the Samogitian language, which in Lithuania is mostly co ...
, Sudovians, Aukštaitians, Dzūkians and Lietuvininkai
The Prussian Lithuanians, or Lietuvininkai (singular: ''Lietuvininkas'', plural: ''Lietuvininkai''), are Lithuanians, originally Lithuanian language speakers, who formerly inhabited a territory in northeastern East Prussia called Prussian Lithu ...
, although the Lietuvinikai are nearly extinct. City dwellers, however, are most often simply called Lithuanians.
Lithuania's ethnic composition has undergone significant changes throughout history. The most significant one of these was the extermination of Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
during the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
. Before World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, approximately 7.5% of Lithuanians were Jewish, referred to as Litvaks
Lithuanian Jews or Litvaks () are Jews with roots in the territory of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania (covering present-day Lithuania, Belarus, Latvia, the northeastern Suwałki and Białystok regions of Poland, as well as adjacent area ...
. The population of Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
was 30% Jewish. Almost all of Lithuania's Jews either were killed by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
or emigrated, and the 2001 census only counted 4007 Jews.
Language
Lithuanian is the official language of Lithuania. Lithuanian, an Indo-European language, closely resembles ancientSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
, and is written using the Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the o ...
. It is considered by scholars that the Lithuanian language retained, with the fewest changes, most of the elements of Proto-Indo-European language. Various dialects of Lithuanian exist, such as High Lithuanian (Aukštaitian) and Low Lithuanian (Samogitian).
During the Lithuanian press ban (1864–1904), Lithuanian was censored by the Russians, and could only be written with the Cyrillic alphabet
, bg, кирилица , mk, кирилица , russian: кириллица , sr, ћирилица, uk, кирилиця
, fam1 = Egyptian hieroglyphs
, fam2 = Proto-Sinaitic
, fam3 = Phoenician
, fam4 = G ...
. Literature in the Lithuanian alphabet was burned and forbidden from publication. Schools, churches, courts, and newspapers faced heavy penalties if Latin text were to be displayed during these years, with violators even exiled to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
.
Religion
Christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
of parts of Lithuania proper in 1387 and of Samogitia
Samogitia or Žemaitija ( Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five cultural regions of Lithuania and formerly one of the two core administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
in 1413, the majority of Lithuanians have been members of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. According to the 2001 census, 79% of Lithuanians are Roman Catholic. Approximately 4.9% of the population are Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
, mainly the Russian minority. Under Article 26 of the Constitution of Lithuania
The Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublikos Konstitucija) defines the legal foundation for all laws passed in the Republic of Lithuania. It was approved in a referendum on 25 October 1992.
History
Statutes of Lithu ...
, persons can freely practice a religion of their choosing.
Catholicism played a significant role in Lithuanian anti-communist resistance under the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
. Several Catholic priests were leaders of the anti-communist movements, and thousands of Latin rite
Latin liturgical rites, or Western liturgical rites, are Catholic rites of public worship employed by the Latin Church, the largest particular church ''sui iuris'' of the Catholic Church, that originated in Europe where the Latin language once ...
crosses
Crosses may refer to:
* Cross, the symbol
Geography
* Crosses, Cher, a French municipality
* Crosses, Arkansas, a small community located in the Ozarks of north west Arkansas
Language
* Crosses, a truce term used in East Anglia and Lincolnshire ...
were placed on the Hill of Crosses
Hill of Crosses ( Lithuanian: ) is a site of pilgrimage about 12 km north of the city of Šiauliai, in northern Lithuania. The precise origin of the practice of leaving crosses on the hill is uncertain, but it is believed that the first cros ...
near Šiauliai
Šiauliai (; bat-smg, Šiaulē; german: Schaulen, ) is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 107,086. From 1994 to 2010 it was the capital of Šiauliai County.
Names
Šiauliai is referred to by various names in different l ...
, despite its being bulldozed in 1961.
Education
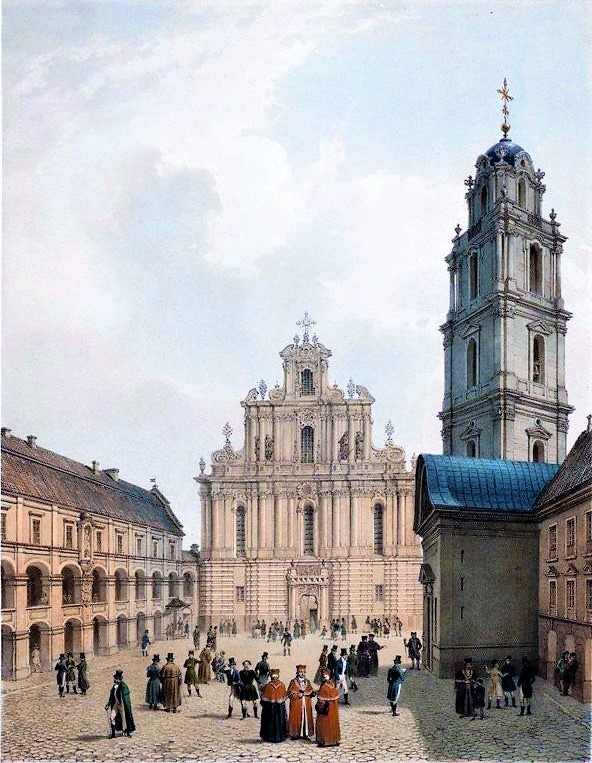 Education in Lithuania exists from pre-school to adult education. Colleges and universities in Lithuania have undergraduate and higher education. Pre-school is for children aged three to six years. After pre-school, children enroll in primary school from seven to ten years of age. At eleven, students begin secondary school until the age of 18. Once the general education is completed, students go to college or university. Students can take the UK exam to study overseas. A bachelor's degree takes four years, traditionally, to complete. A master's takes one to two years to complete; and a doctoral degree takes four years. Lithuania's oldest university is
Education in Lithuania exists from pre-school to adult education. Colleges and universities in Lithuania have undergraduate and higher education. Pre-school is for children aged three to six years. After pre-school, children enroll in primary school from seven to ten years of age. At eleven, students begin secondary school until the age of 18. Once the general education is completed, students go to college or university. Students can take the UK exam to study overseas. A bachelor's degree takes four years, traditionally, to complete. A master's takes one to two years to complete; and a doctoral degree takes four years. Lithuania's oldest university is Vilnius University
Vilnius University ( lt, Vilniaus universitetas) is a public research university, oldest in the Baltic states and in Northern Europe outside the United Kingdom (or 6th overall following foundations of Oxford, Cambridge, St. Andrews, Glasgow and ...
, which was founded in 1579.
Food and lifestyle
 Lithuanian cuisine features the products suited to its cool and moist northern climate:
Lithuanian cuisine features the products suited to its cool and moist northern climate: barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
, potatoes
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern United ...
, rye, beet
The beetroot is the taproot portion of a beet plant, usually known in North America as beets while the vegetable is referred to as beetroot in British English, and also known as the table beet, garden beet, red beet, dinner beet or golden beet ...
s, greens, berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, rasp ...
, and mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans.
The standard for the name "mushroom" is t ...
s are locally grown, and dairy products are one of its specialities. Since it shares its climate and agricultural practices with Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
, Lithuanian cuisine has much in common with other Eastern European and Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
cuisines. Nevertheless, it has its own distinguishing features, which were formed by a variety of influences during the country's long and difficult history. German traditions also influenced Lithuanian cuisine, introducing pork and potato dishes, such as potato pudding ( or ) and potato sausages (), as well as the baroque tree cake known as . The most exotic of all the influences is Eastern (Crimean Karaites
The Crimean Karaites or Krymkaraylar (Crimean Karaim: Кърымкъарайлар, ''Qrımqaraylar'', singular къарай, ''qaray''; Trakai dialect: ''karajlar'', singular ''karaj''; he, קראי מזרח אירופה; crh, Qaraylar; ), a ...
) cuisine, and the dishes and are popular in Lithuania. Torte Napoleon was introduced during Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's passage through Lithuania in the 19th century. Some traditional meals are (also called ) - potato dumplings, - cold borscht (beetroot soup), - dark rye bread, - stuffed cabbage rolls, - potato pancakes, (fermented rye bread drink), and - smoked fatback.
Media and art
Art and museums

 Lithuania's art community is famous for
Lithuania's art community is famous for Mikalojus Konstantinas Čiurlionis
Mikalojus Konstantinas Čiurlionis ( pl, Mikołaj Konstanty Czurlanis – ) was a Lithuanian painter, composer and writer.
Čiurlionis contributed to symbolism and art nouveau, and was representative of the fin de siècle epoch. He has been ...
(1875–1911). Čiurlionis was a nationally renowned musician and artist in Lithuania. His symphonic compositions, Jūra ("The sea") and Miške ("In the forest"), were the first full-length pieces from a Lithuanian musician. Jūra ("The sea") and Miške ("In the forest") were composed to represent Lithuania's landscape. After Čiurlionis's death, the 2420 Čiurlionis asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
honors his achievements after being discovered in 1975.
A large number of museums exist in Lithuania. The Lithuanian Art Museum
Lithuanian National Museum of Art is the largest national museum in Lithuania collecting, restoring, and conserving art as well as historical objects of cultural value while presenting artefacts of national importance in an astonishing number of ...
was founded in 1933 and is the largest museum of art preservation and display in Lithuania. The Palanga Amber Museum
The Palanga Amber Museum ( lt, Palangos gintaro muziejus), near the Baltic Sea in Palanga, Lithuania, is a branch of the Lithuanian Art Museum. It is housed in the restored 19th-century Tiškevičiai Palace and is surrounded by the Palanga Botan ...
is a subsidiary of the Lithuanian Art Museum. Various amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In Ma ...
pieces comprise a major part of the museum. In total, 28,000 pieces of amber are displayed, and about 15,000 contain inclusions of insects, spiders, or plants. Some 4,500 amber pieces in the museum are used for artwork and jewelry.Palangos gintaro muziejusAntanas Tranyzas: The Amber Museum of Palanga
Retrieved on March 29, 2007. The
Lithuanian Museum of Ancient Beekeeping
The Lithuanian Museum of Ancient Beekeeping (''Senovinės bitininkystės muziejus''), established in 1984 near Stripeikiai in northeastern Lithuania, displays the history of beekeeping in the area.
The museum, part of Aukštaitija National Par ...
displays various forms of bee hive
A beehive is an enclosed structure in which some honey bee species of the subgenus '' Apis'' live and raise their young. Though the word ''beehive'' is commonly used to describe the nest of any bee colony, scientific and professional literature ...
s. The Grūtas Park contains Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
-era relics and statues including those of Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
and Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
.
Music
Lithuania has a long history of folk, popular and classical musical development. Lithuanian folk music is based primarily around polyphonic music played on flutes, zithers (kanklės) and other instruments.Folk
 Lithuanian folk music is based around songs (), which include romantic, wedding songs, as well as work songs and more archaic war songs. Traditional vocal music is held in high esteem on a world scale: Lithuanian song fests and multipart songs are on the
Lithuanian folk music is based around songs (), which include romantic, wedding songs, as well as work songs and more archaic war songs. Traditional vocal music is held in high esteem on a world scale: Lithuanian song fests and multipart songs are on the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
's representative list of the Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity. Folk songs were performed either in groups or alone, and in parallel chords or unison
In music, unison is two or more musical parts that sound either the same pitch or pitches separated by intervals of one or more octaves, usually at the same time. ''Rhythmic unison'' is another term for homorhythm.
Definition
Unison or per ...
. Duophonic
Duophonic sound was a trade name for a type of audio signal processing used by Capitol Records on certain releases and re-releases of mono recordings issued during the 1960s and 1970s. In this process monaural recordings were reprocessed into a ...
songs are common in the renowned tradition of . Another style of Lithuanian folk music is called , a kind of round dance. Instrumentation includes , a kind of zither
Zithers (; , from the Greek word ''cithara'') are a class of stringed instruments. Historically, the name has been applied to any instrument of the psaltery family, or to an instrument consisting of many strings stretched across a thin, flat ...
that accompanies , , waltz
The waltz ( ), meaning "to roll or revolve") is a ballroom and folk dance, normally in triple ( time), performed primarily in closed position.
History
There are many references to a sliding or gliding dance that would evolve into the wa ...
es, quadrille
The quadrille is a dance that was fashionable in late 18th- and 19th-century Europe and its colonies. The quadrille consists of a chain of four to six '' contredanses''. Latterly the quadrille was frequently danced to a medley of opera melodie ...
s and polka
Polka is a dance and genre of dance music originating in nineteenth-century Bohemia, now part of the Czech Republic. Though associated with Czech culture, polka is popular throughout Europe and the Americas.
History
Etymology
The term ...
s, and fiddle
A fiddle is a bowed string musical instrument, most often a violin. It is a colloquial term for the violin, used by players in all genres, including classical music. Although in many cases violins and fiddles are essentially synonymous, th ...
s, (including a bass fiddle called the ), a kind of whistle
A whistle is an instrument which produces sound from a stream of gas, most commonly air. It may be mouth-operated, or powered by air pressure, steam, or other means. Whistles vary in size from a small slide whistle or nose flute type to a larg ...
called the and, similar in sound to clarinet
The clarinet is a musical instrument in the woodwind family. The instrument has a nearly cylindrical bore and a flared bell, and uses a single reed to produce sound.
Clarinets comprise a family of instruments of differing sizes and pitches ...
, ; recent importations, beginning in the late 19th century, including the concertina
A concertina is a free-reed musical instrument, like the various accordions and the harmonica. It consists of expanding and contracting bellows, with buttons (or keys) usually on both ends, unlike accordion buttons, which are on the front.
The ...
, accordion
Accordions (from 19th-century German ''Akkordeon'', from ''Akkord''—"musical chord, concord of sounds") are a family of box-shaped musical instruments of the bellows-driven free-reed aerophone type (producing sound as air flows past a reed ...
and . Sutartinė is accompanied by the , a form of panpipes
A pan flute (also known as panpipes or syrinx) is a musical instrument based on the principle of the closed tube, consisting of multiple pipes of gradually increasing length (and occasionally girth). Multiple varieties of pan flutes have been ...
played by a group of people, as well as wooden trumpets ( and ). The is an extremely important folk instrument, which differs in the number of strings and performance techniques across the country. Other traditional instruments include the (whistle), drum
The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone. Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a she ...
s and (a percussion instrument like a gong
A gongFrom Indonesian and ms, gong; jv, ꦒꦺꦴꦁ ; zh, c=鑼, p=luó; ja, , dora; km, គង ; th, ฆ้อง ; vi, cồng chiêng; as, কাঁহ is a percussion instrument originating in East Asia and Southeast Asia. Gongs ...
), (bagpipe
Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, ...
) and the (a musical bow
The musical bow (bowstring or string bow, a subset of bar zithers) is a simple string instrument used by a number of South African peoples, which is also found in the Americas via slave trade. It consists of a flexible, usually wooden, stick 1 ...
made from a pig's bladder
Pig bladder (also pig's bladder) is the urinary bladder of a domestic pig, similar to the human urinary bladder. Today, this hollow organ has various applications in medicine, and in traditional cuisines and customs. Historically, the pig bladde ...
filled with dried peas).
Rock
In the 1980s, rock bands Foje, Antis, andBix
Leon Bismark "Bix" Beiderbecke (March 10, 1903 – August 6, 1931) was an American jazz cornetist, pianist and composer.
Beiderbecke was one of the most influential jazz soloists of the 1920s, a cornet player noted for an inventive lyrical app ...
made a big impact in Lithuania.
Cinema and theatre
 Lithuania has a lively drama scene. Many
Lithuania has a lively drama scene. Many film festivals
A film festival is an organized, extended presentation of films in one or more cinemas or screening venues, usually in a single city or region. Increasingly, film festivals show some films outdoors. Films may be of recent date and, depending upo ...
exist, such as Kino Pavasaris and the AXX Commercial Film Festival Contest. Film tradition has emerged throughout Lithuania's occupation by the Soviet Union. A popular Lithuanian film classic is ''Velnio Nuotaka'', which is based upon folk tales.
A major theater in Lithuania is the Lithuanian National Drama Theater. Another theatre, the Vilnius Little Theatre, was founded by Rimas Tuminas. Vilnius Little Theatre produces Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
plays and other productions.Bousfield 2004, ''Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia & Lithuania'', p. 55. Actors are being taught in the Lithuanian Academy of Music and Theatre
The Lithuanian Academy of Music and Theatre in Vilnius, Lithuania, is a state-supported conservatory that trains students in music, theatre, and multimedia arts.
History
Composer Juozas Naujalis founded a music school in 1919 in Kaunas. This ...
, which was founded in 1919 by Juozas Naujalis
Juozas Naujalis (9 April 1869 in Raudondvaris – 9 September 1934 in Kaunas) was a Lithuanian composer, organist and choir conductor. He is acclaimed as Lithuanian music patriarch.
Biography
Naujalis studied Warsaw Institute of Music and in Rege ...
as the Kaunas Music School. The academy was renamed in 2004.IntroductionLithuanian Academy of Music and Theatre. Retrieved on October 17, 2008. Several directors are important to Lithuania's theatre scene.
Eimuntas Nekrošius
Eimuntas Nekrošius (November 21, 1952 – November 20, 2018) was a Lithuanian theatre director.
Biography
Early life
Nekrošius was born in Pažobris village, Raseiniai district municipality, Lithuania on November 21, 1952.
Career
In 1978, Nek ...
is a major part of Lithuania's theatre movement and has a theatre company, Meno Fortas
Meno Fortas is a theatrical production facility and theater group in Vilnius formed and directed by Lithuanian Eimuntas Nekrošius since 1998. It was specifically created for the production of works under this director, but is also active in the f ...
. He has produced Shakesperian plays, such as ''Macbeth
''Macbeth'' (, full title ''The Tragedie of Macbeth'') is a tragedy by William Shakespeare. It is thought to have been first performed in 1606. It dramatises the damaging physical and psychological effects of political ambition on those w ...
'', ''Othello
''Othello'' (full title: ''The Tragedy of Othello, the Moor of Venice'') is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare, probably in 1603, set in the contemporary Ottoman–Venetian War (1570–1573) fought for the control of the Island of Cypru ...
'', and ''Hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
''. Oskaras Koršunovas
Oskaras Koršunovas (born 6 March 1969) is a Lithuanian theatre director.
Biography
Oskaras Koršunovas was born on March 6, 1969, in Vilnius, Lithuania. He began his career as a theatre director in 1994 at the Lithuanian Academy of Music a ...
is another acclaimed contemporary director, producing musicals, studio performances, and plays, including ''Hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
'' and ''Midsummer Night's Dream
''A Midsummer Night's Dream'' is a comedy written by William Shakespeare 1595 or 1596. The play is set in Athens, and consists of several subplots that revolve around the marriage of Theseus and Hippolyta. One subplot involves a conflict amon ...
''.
Television
The first channel in theLithuanian language
Lithuanian ( ) is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.8 millio ...
was introduced in 1957. Lithuania has 8 main channels, 24 regional channels and 2 non-Lithuanian channels, with Lithuanian language
Lithuanian ( ) is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.8 millio ...
translation. The national channel is Lithuanian National Radio and Television (''Lietuvos televizija''; Television of Lithuania).
Sports
 There are eighty Olympic and non-Olympic sports federations in Lithuania. Among the most popular sports in Lithuania are
There are eighty Olympic and non-Olympic sports federations in Lithuania. Among the most popular sports in Lithuania are basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appr ...
, football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
, athletics
Athletics may refer to:
Sports
* Sport of athletics, a collection of sporting events that involve competitive running, jumping, throwing, and walking
** Track and field, a sub-category of the above sport
* Athletics (physical culture), competi ...
, and cycling
Cycling, also, when on a two-wheeled bicycle, called bicycling or biking, is the use of cycles for transport, recreation, exercise or sport. People engaged in cycling are referred to as "cyclists", "bicyclists", or "bikers". Apart from t ...
. Professional sportsmen and trainers are educated in the Lithuanian Academy of Physical Education.
On October 1, 1932, the Department of Physical Education and Sports was founded. The department supports Lithuanian athletics and promotes physical education. Lithuania's National Olympic Committee supports Lithuania's Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece b ...
athletes and is led by Arturas Poviliunas.
Discus throw
The discus throw (), also known as disc throw, is a track and field event in which an athlete throws a heavy disk (mathematics), disc—called a discus—in an attempt to mark a farther distance than their competitors. It is an classical antiqui ...
Olympic athlete Virgilijus Alekna
Virgilijus Alekna (; 13 February 1972) is a Lithuanian former discus thrower and politician. He won medals at the 2000, 2004 and 2008 Olympics, including two golds.
After retiring from athletics, Alekna was elected to the national parliament, t ...
is a two-time gold winner and medalist. Alekna was named UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
Champion for Sport in 2007.
 Lithuania's national basketball team,
Lithuania's national basketball team, football team
A football team is a group of players selected to play together in the various team sports known as football. Such teams could be selected to play in a match against an opposing team, to represent a football club, group, state or nation, an All-st ...
and rugby union team compete internationally. The country has produced several world-class basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appr ...
players, such as Arvydas Sabonis
Arvydas Romas Sabonis (; born December 19, 1964) is a Lithuanian former professional basketball player and businessman. Recognized as one of the best European players of all time, he won the Euroscar six times and the Mr. Europa Award twice. He p ...
, Žydrūnas Ilgauskas
Zydrunas Ilgauskas ( lt, link=no, Žydrūnas Ilgauskas; ; born June 5, 1975) is a Lithuanian-born American former professional basketball player who played the center position. The 7'3" Ilgauskas played for the Cleveland Cavaliers of the Nationa ...
and Linas Kleiza
Linas Kleiza (; born January 3, 1985) is a Lithuanian professional basketball executive and former player. Standing at , he played at the small forward and power forward positions. In 2010, he was the Alphonso Ford EuroLeague Top Scorer Trophy ...
.
Literature and journalism
Lithuania's literature is based upon folklore tradition. Song books began publishing in the sixteenth century. The first Lithuanian book was ''Katekizmas'' (''Simple Words of Catechism'') by Martynas Mažvydas in 1547. A archival site of Lithuanian literature and folklore is the Institute of Lithuanian Literature and Folklore inVilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
.
Newspapers and magazines are popular in Lithuania. Lithuania's biggest selling newspaper is ''Lietuvos Rytas''. Whereas, ''Respublika'' and ''Vakaro Zinios'' are tabloid magazines. English language magazine publications are translated into Lithuanian for local consumers.Bousfield 2004, ''Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia & Lithuania'', p. 56.
Architecture and housing
 Several famous Lithuania-related architects are notable for their achievements in the field of architecture.
Several famous Lithuania-related architects are notable for their achievements in the field of architecture. Johann Christoph Glaubitz
Johann Christoph Glaubitz ( – 30 March 1767) was an architect of German descent who is generally considered to be the most prominent Baroque architect in the lands of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Early life
Glaubitz was born in Sc ...
, Marcin Knackfus
Marcin Knackfus (, c. 1742 – c. 1821) was a Polish–Lithuanian Neoclassical architect of German descent. Born near Warsaw, he worked in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and particularly in its capital Vilnius. He was a tutor of Laurynas Guceviči ...
, Laurynas Gucevičius
Laurynas Gucevičius ( pl, Wawrzyniec Gucewicz; 1753–1798) was an 18th-century architect from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and all of his designs were built there.
In his youth he travelled to Italy and Paris and other countries in Western Eur ...
and Karol Podczaszyński
Karol Podczaszyński ( lt, Karolis Podčašinskis) (7 November 1790 – 19 April 1860) was a Polish- Lithuanian leading Vilnius architect, a representative of the neoclassical architecture and a professor of the Vilnius University, as well as on ...
were instrumental in introducing Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
and neoclassical architectural movements to the Lithuanian architecture during the seventeenth to nineteenth centuries.
Lithuania is also known for numerous castles. About twenty castles exist in Lithuania. Some castles had to be rebuilt or survive partially. Lithuanian village life has existed since the days of Vytautas the Great
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
. Zervynos and Kapiniškės are two of many ethnographic villages in Lithuania.
Forty percent of Lithuania's population live in Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
, Kaunas
Kaunas (; ; also see other names) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Trakai ...
, Klaipėda
Klaipėda (; ; german: Memel; pl, Kłajpeda; russian: Клайпеда; sgs, Klaipieda) is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. The capital of the eponymous county, it is the third largest city and the only major seaport in Lithuan ...
, Alytus, Panevėžys
Panevėžys (; Latin: ''Panevezen''; pl, Poniewież; yi, פּאָנעװעזש, ''Ponevezh''; see also other names) is the fifth largest city in Lithuania. As of 2011, it occupied with 113,653 inhabitants. As defined by Eurostat, the population ...
, and Šiauliai
Šiauliai (; bat-smg, Šiaulē; german: Schaulen, ) is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 107,086. From 1994 to 2010 it was the capital of Šiauliai County.
Names
Šiauliai is referred to by various names in different l ...
. Even though population density has grown within Lithuania, overall, population has declined due to low birth rates
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; populati ...
and higher death rates
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of de ...
. Between 1996 and 2001, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
financed the Lithuania Energy Efficiency Housing Project to renovate thermal temperatures in some of Lithuania's houses, due to Lithuania's cold climate.
Holidays
 The official holidays are found in Article 162 of the ''Labour Code of the Republic of Lithuania.'' The holidays are as follows:
* January 1:
The official holidays are found in Article 162 of the ''Labour Code of the Republic of Lithuania.'' The holidays are as follows:
* January 1: New Year's Day
New Year's Day is a festival observed in most of the world on 1 January, the first day of the year in the modern Gregorian calendar. 1 January is also New Year's Day on the Julian calendar, but this is not the same day as the Gregorian one. Wh ...
* February 16: Day of Re-establishment of the State of Lithuania (1918)
* March 11: Day of Restitution of Independence of Lithuania (from the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, 1990)
* First Sunday and Monday of spring with full moon Easter
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samuel ...
* May 1: International Labor Day
* First Sunday in May: Mother's Day
Mother's Day is a celebration honoring the mother of the family or individual, as well as motherhood, maternal bonds, and the influence of mothers in society. It is celebrated on different days in many parts of the world, most commonly in the ...
* First Sunday in June: Father's Day
Father's Day is a holiday of honoring fatherhood and paternal bonds, as well as the influence of fathers in society. In Catholic countries of Europe, it has been celebrated on 19 March as Saint Joseph's Day since the Middle Ages. In the United ...
* June 24: St. John's Day hristian name Day of Dew riginal pagan nametraditions. (aka: Midsummer Day
Midsummer is a celebration of the season of summer usually held at a date around the summer solstice. It has pagan pre-Christian roots in Europe.
The undivided Christian Church designated June 24 as the feast day of the early Christian martyr S ...
, Saint Jonas Day
Saint Jonas' Festival, also known as ''Rasos'' (''Dew Holiday''), ''Joninės'', ''Kupolė'', Midsummer Day or Saint John's Day) is a midsummer folk festival celebrated on 24 June all around Lithuania. While midsummer day is celebrated throughout ...
)
* July 6: Statehood Day
* August 15: Assumption Day
* November 1: All Saints' Day
All Saints' Day, also known as All Hallows' Day, the Feast of All Saints, the Feast of All Hallows, the Solemnity of All Saints, and Hallowmas, is a Christian solemnity celebrated in honour of all the saints of the church, whether they are know ...
* December 25 and December 26: Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus, Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by country, around t ...
See also
* History of Lithuanian culture *Lithuanian mythology
Lithuanian mythology ( lt, Lietuvių mitologija) is the mythology of Lithuanian polytheism, the religion of pre-Christian Lithuanians. Like other Indo-Europeans, ancient Lithuanians maintained a polytheistic mythology and religious structure. ...
* List of museums in Lithuania
References
Sources
* {{Culture of Europe